Vaginal Cyst- Meaning, Types, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Vaginal cysts are soft lumps formed on the vaginal walls. The vagina is part of the female reproductive system. The vaginal opening is surrounded by labia, where the vaginal cysts can be felt. The vaginal cyst may also be present inside the vagina. Cysts are tissue pockets filled with pus, fluid, air, or other materials. Vaginal cysts mostly contain pus, fluid, or air. They occur mainly in reproductively active women.
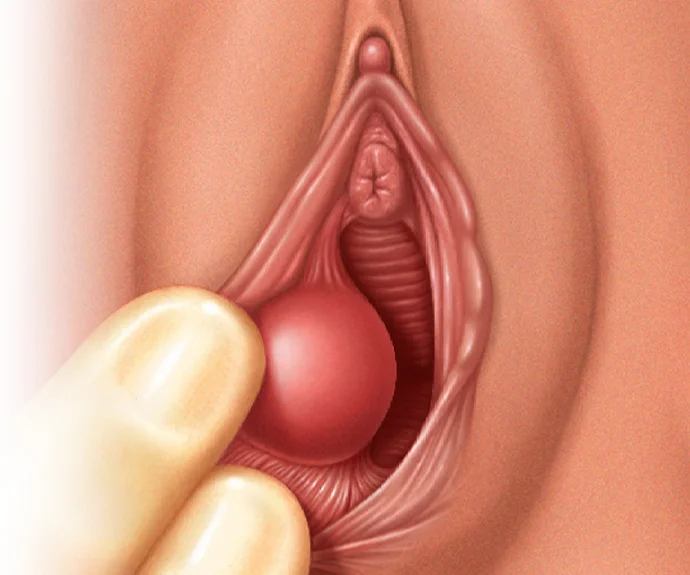
WHAT IS A VAGINAL CYST
A vaginal cyst is a bump containing air, mucous, or pus on the vaginal walls. Vaginal cysts that are small mostly go undetected and do not pose any harm to health. In most cases, vaginal cysts are found incidentally during a routine pelvic examination. However, larger cysts can cause discomfort or pain during sex, or difficulty with urination or bowel movements. The sac-like structure develops in the vaginal wall or around the vaginal opening and is usually filled with fluid, and its size can range from tiny to several centimeters in diameter.
Vaginal cysts are generally benign, meaning they are not cancerous, and they can develop at any age.

TYPES OF VAGINAL CYSTS
Inclusion cysts
Type of cyst formed in the lower back of the vaginal walls. These types of cysts are small in size and mostly go unnoticed. Inclusion cysts are the most common type of cyst developing on the vaginal walls due to vaginal injuries in the process of childbirth or certain surgery.
1
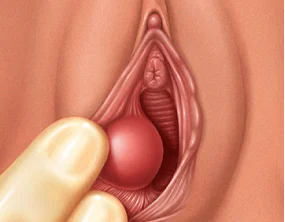
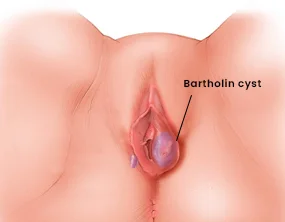
Bartholin cyst
Type of cyst filled with infectious fluid present on the vaginal opening where Bartholin's glands are located. The bartholin gland is responsible for secreting lubricating fluid inside the vagina and on its outer lips.
2
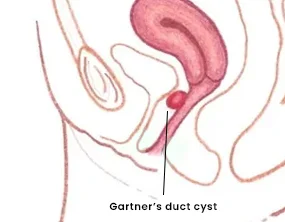
Gartner’s duct cyst
The type of cyst formed as a result of the remaining glands of the developing embryo that must have disappeared in normal circumstances. These leftover glands or ducts lead to the formation of cysts inside the vagina.
3
Sebaceous cyst
Type of cyst that develops due to blockage of sebaceous glands (responsible for oil production) in external genitalia or vulva.
4

Muller’s cyst
Another type of vaginal cyst is commonly found on the walls of the vagina. These may contain mucus and develops due to materials that remain in the course of the development of a baby in the uterus.
5
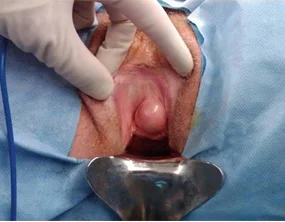
CAUSES
- Vaginal injuries
- Blocked vaginal ducts or glands
- Vaginal infections
HOW IS IT FORMED
Vaginal cysts are formed when a gland or duct in the vaginal wall becomes blocked, causing the secretion of fluids to accumulate and form a sac. They can also be caused by injury or trauma to the vaginal wall, or as a result of an infection. Some types of vaginal cysts include Bartholin's gland cysts, Gartner's duct cysts, and Skene's gland cysts. There are different types of vaginal cysts formed due to various reasons. Blockage of ducts or glands present in and around the vagina causes accumulations of fluids, or pus-forming lumps called vaginal cysts. Vaginal injuries during the process of childbirth or surgeries cause the trapping of tissues on the vaginal surface, leading to the formation of vaginal cysts.
The symptoms of a vaginal cyst can vary depending on the size and location of the cyst. In most cases, vaginal cysts do not cause any symptoms and are discovered during routine pelvic exams. However, larger cysts may cause discomfort, pain during sex, or difficulty with urination.

SYMPTOMS
- Small bump on the vagina
- Painful Sex
- Discomfort in the genitals
- Fever and pain (in case of infected cyst)
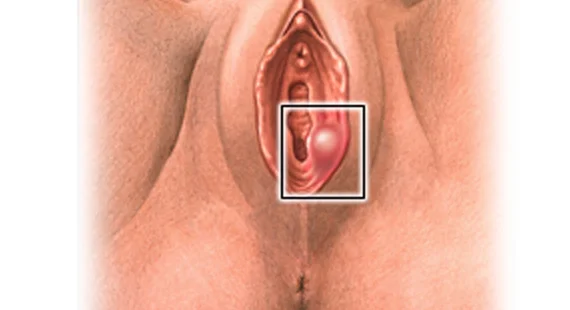
DIAGNOSIS
Physical examination-Healthcare providers make the diagnosis of a vaginal cyst by looking at or touching the cyst. The cyst is examined in timely intervals in order to check if it grows in size.
To rule out that vaginal cysts is cancerous :
- Biopsy
- Vaginal fluid test
- Ultrasound - Imaging test to look for the size of the vaginal cyst
- MRI - It is done to look for the changes in size or texture of the vaginal cyst and check if it is a tumour.
DO's
DONT's
TREATMENTS
NON SURGICAL TREATMENTS
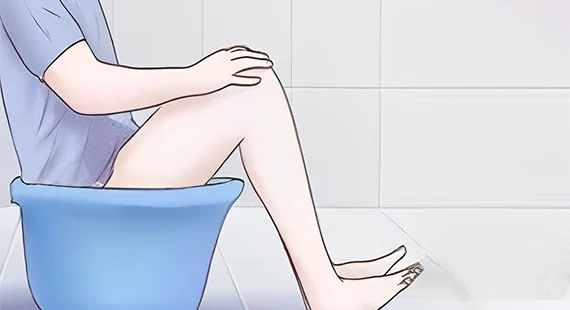
Sitz Bath
Sitting in a bathtub containing lukewarm water gives comfort and helps in healing the vaginal cyst. Several sittings in a day for 3-4 minutes prove to be beneficial.
Antibiotic treatment
To help deal with the infected cyst, antibiotics are given to relieve inflammation, swelling and pus due to bacterial infections in the vaginal cyst.
SURGICAL TREATMENTS
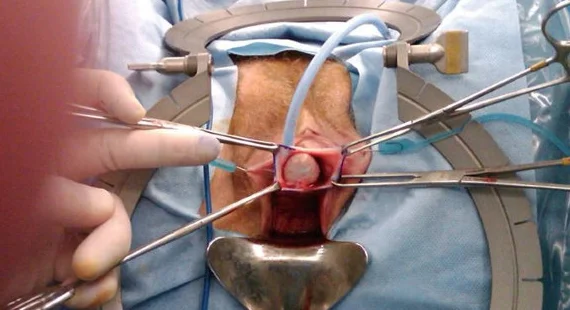
Draining
A vaginal cyst is drained by inserting a catheter ( a small tube) inside the vaginal cyst to drain out the fluid or pus in the vaginal cyst.
Marsupialization
The process of surgically opening the cyst and draining its fluid or pus, and stitching it from one side only is called marsupialization.
RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS
There is always a risk of infection of vaginal cysts that can lead to various complications. There is also a risk of developing abnormal or cancerous outgrowth of vaginal cysts.
Complications:
- Fever
- Painful sex
- Foul discharge
- Discomfort
- Pus collection
IF LEFT UNTREATED
If vaginal cysts are left untreated, they may become enlarged, swollen and filled with pus or fluids upon getting infected. It is crucial to diagnose it to rule out if it is cancerous.
COST
Surgical treatment of vaginal cysts costs between ₹15,000 to ₹45,000. The cost varies depending on the type of surgical treatment procedure.
Financial Options

INSURANCE COVERAGE
The cost of insurance for the treatment of a vaginal cyst is covered only when surgery is required to remove the vaginal cyst. Most of the time, the insurer will cover a particular amount for the surgery. However, the amount of coverage depends on the type of policy. It is essential to know that treatments other than surgical treatments will not be covered under health insurance.

Know more about Vaginal cyst
A vaginal cyst is a type of fluid-filled sac that develops inside or just outside the vagina. These cysts are usually benign (non-cancerous) and can vary in size from very small to quite large. In most cases, vaginal cysts do not cause any symptoms and are found incidentally during a routine pelvic examination. However, larger cysts can cause discomfort or pain during sex, or difficulty with urination or bowel movements.
Glamyo Health is a healthcare brand operating in the fields of elective and cosmetic surgeries, with a chain of hospitals and clinics operating in 40+ cities all over India.
Looking for effective treatment of vaginal cysts? Glamyo Health provides the best and safest options for vaginal cyst removal. Know the best Gynecologist and surgeons in Delhi and Gynecology clinics.
Read about the Advanced surgical options available to get rid of vaginal cysts permanently. If you have questions about how long does it take to get rid of a vaginal cyst, know the estimated time of Recovery. We provide you with our happy patient reviews to know their journey throughout the treatment.
 New Delhi
New Delhi  Bangalore
Bangalore  Mumbai
Mumbai  Hyderabad
Hyderabad  Pune
Pune  Chennai
Chennai 
