Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Diabetic foot ulcers are becoming a major condition, rapidly being detected in patients with Diabetic conditions. The number of people becoming affected by it is rising, and this is causing health complications in a person.
The recent finding states that some of the diabetic patients with Diabetic foot ulcers are urgently rushed to the hospital. Thus, the need to understand and immediately treat a diabetic foot ulcer has become crucial.
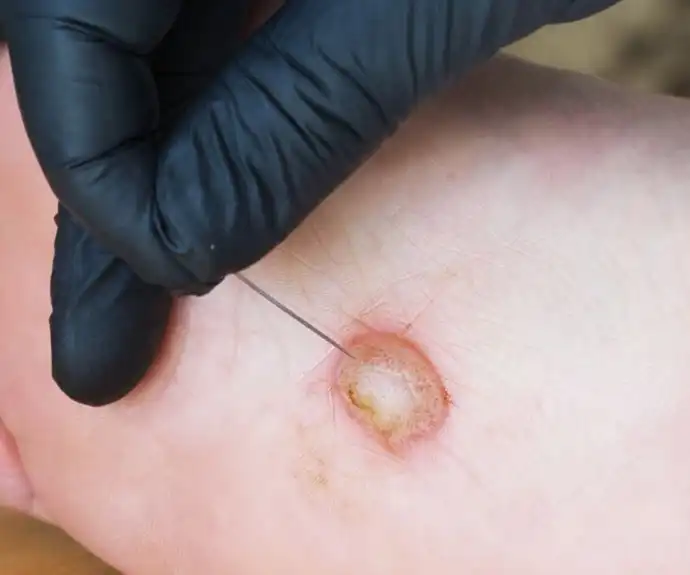
WHAT ARE DIABETIC FOOT ULCERS?
A diabetic foot ulcer is a wound or a sore opening, usually formed and found in the foot area at the bottom of the feet. A diabetic foot ulcer is found in 10% to 15% of patients diagnosed with diabetes.
To detect a diabetic foot ulcer, look for a red round-shaped creature formed on the foot skin and is bordered with a thickened round caused to the skin. Though the small-sized ulcers are not much visible, larger-sized ulcers are easy to spot.
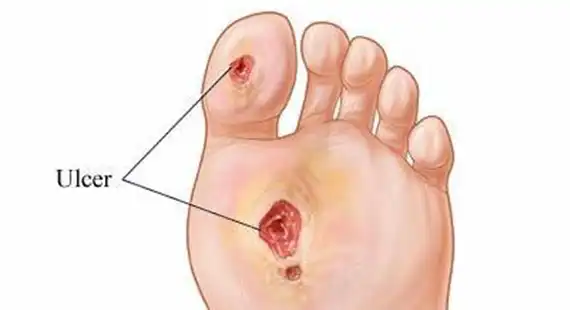
CAUSES
- Foot deformities
- Ill-fitted or tightly-fitting footwear
- Poor glycemic control
- Poor circulation of blood
- Underlying peripheral neuropathy
- Dry skin or cracked skin
- Bad foot hygiene and improper foot care
How Is it Formed
Diabetic foot ulcers, commonly found in many diabetic patients, are formed due to the collective effect of certain factors, which are the duration of diabetes, poor circulation, lack of sensing or feeling in the foot, irritation due to pressure, swelling or friction, due to past trauma, or injury.
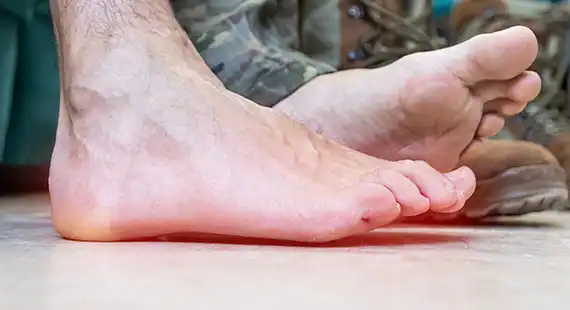
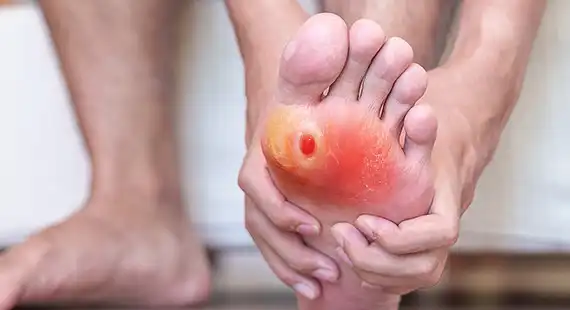
SYMPTOMS
- Mild to intense pain
- Foul smell
- Redness in the area
- Swollen skin
- Skin affected with discolouration.
- Discharge of pus or fluid
- Toenail or skin changes such as blisters, cuts, calluses and sores.
DIAGNOSIS
- Medical history
- Conducting physical medical exam
- X-Ray test
- MRI scanning test
- Blood test
DO's
DONT's
TREATMENTS
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS
Wound care - Diabetic wounds requires proper care and dressing. It is advised to apply topical antibiotic ointment to the wounds.
Physiotherapy - To improve blood circulation in feet, massage, hot or cold therapy and exercises are important.
Medications - Pain and inflammation relieving analgesics, corticosteroids, and anti-inflammatories
SURGICAL TREATMENTS
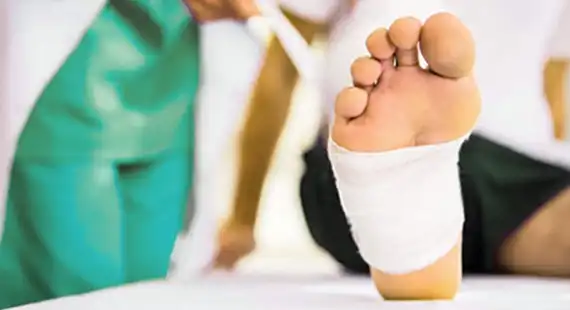
Usually, diabetic foot ulcers are treated non-surgically only. Especially when the ulcer is not severe, some diabetic foot ulcers can require a surgical approach.
In such situations, the surgery options available can be associated with deformities correction like bunions, hammer toes and bony bumps and excision or shaving of the bones.
- Achilles tendon lengthening
- Debridement
- Vascular surgery
Risk and Complications
- Different Foot deformities
- Various skin-related infections
- Forefoot gangrene or full foot gangrene
- Sepsis
- Sudden abscess formation
- Results in foot amputation
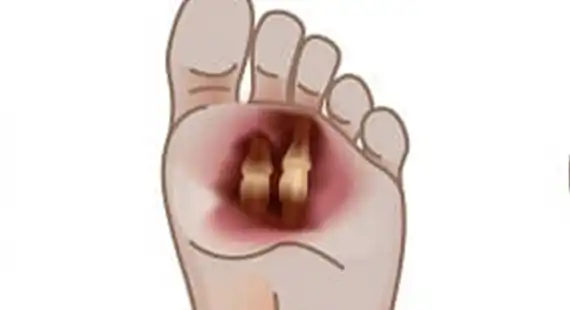
IF LEFT UNTREATED
If a diabetic foot ulcer is detected in a patient and is left interested or neglected for too long, it can raise major complications. These complications can be ischemia that can lead to tissue death, and skin infections.
INSURANCE COVERAGE
Treatment for Diabetic foot ulcer is covered under health insurance. However, the amount of coverage will depend on the type of policy, and the treatment advised by the doctor.
It is important to know that medical treatment for diabetic foot ulcers will not be covered under the insurance policy, it will only cover the cost or expenses of the surgical treatment, but to claim this, you will have to be hospitalized for 24 hours.

DIABETIC FOOT ULCERS
Diabetic foot ulcers are open wounds that occur in almost 25% of diabetic patients. Half of these patients require hospitalization because of infection or other ulcer-associated complications. Foot ulcers are not managed by diet, exercise, and insulin injections.
Prevention of diabetic foot ulcers involves maintaining good foot hygiene, regularly inspecting the feet for cuts or sores, wearing properly fitting shoes and socks, and avoiding walking barefoot. Maintaining good blood sugar control, quitting smoking, and staying physically active can also reduce the risk of developing these ulcers.
It is important to seek medical attention promptly if you have diabetes and notice any signs of a foot ulcer or other foot injury. With proper care and management, diabetic foot ulcers can often be treated successfully and the risk of complications minimized.
 New Delhi
New Delhi  Bangalore
Bangalore  Mumbai
Mumbai  Hyderabad
Hyderabad  Pune
Pune  Chennai
Chennai 
